Cryptocurrency
FL Stat § 896.101 includes virtual currency in its definition of monetary instruments. FL Stat § 560.103 defines a money transmitter as an entity that “receives currency, monetary value, or payment instruments for the purpose of transmitting the same by any means https://helpforerror.com/.” FL Stat § 560.125 states that “A person may not engage in the business of a money services business or deferred presentment provider in this state unless the person is licensed.” State v. Espinoza (2019) found that this licensing requirement includes those conducting cryptocurrency transactions, even two-party, individual, ones. The deadline to comply with the Espinoza ruling was the last day of 2021. On May 12, 2022, Governor Ron DeSantis signed HB 273 into law, which revises many of Florida’s existing cryptocurrency statutes. The law defines virtual currency under FL Stat § 560.103 and explicitly includes virtual currency transmitters in the scope of FL Stat § 560. It clarifies FL Stat § 560.125 and partially undoes the Espinoza ruling, stating that money transmitter licenses are only required for “intermediaries” that “transmit…virtual currency from one person to another location or person,” and who have “the ability to unilaterally execute or indefinitely prevent a transaction.” Therefore, two-party, individual transactions will no longer require licensing, but major exchanges still will. HB 273 eases restrictions on these exchanges by excluding virtual currency from the definition of payment instrument and regulating exchanges solely under money service business regulations. It also allows exchanges to only hold virtual currency of the same type and amount owed instead of requiring additional cash reserves. The law takes effect on January 1, 2023, and will solidify Florida as a crypto-friendly state. FL Stat § 559.952 establishes a Financial Technology Sandbox “to allow financial technology innovators to test new products and services in a supervised, flexible regulatory sandbox using exceptions to specified general law and waivers of the corresponding rule requirements under defined conditions.” Under this law, developing blockchain or cryptocurrency businesses with sandbox permission are exempt from needing a money transmitter license during the license period and face less regulatory scrutiny.
Today, South Korea’s Financial Services Commission (FSC) is working on the Digital Asset Basic Act, expected to be introduced later in 2023, an all-encompassing effort to reduce crypto crime and bring more clarity to the legitimate players in the space.
On September 21, 2021, the U.S. Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) issued an updated advisory about the sanctions risks of facilitating ransomware payments using cryptocurrencies. OFAC’s advisory reminds organizations that it applies a strict liability standard when imposing civil penalties for sanctions violations. Thus, organizations may be liable for making a ransomware payment even if they do not know that the recipient has been designated a malicious cyber actor by OFAC. If a payment is made to a sanctioned entity, the advisory noted that OFAC would consider in its enforcement response: (1) whether the organization took meaningful steps to reduce the risk of extortion by a sanctioned actor, citing practices highlighted in the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency’s (CISA) September 2020 Ransomware Guide; and (2) whether the organization reported the attack “to appropriate U.S. government agencies,” as well as “the nature and extent of cooperation with OFAC, law enforcement, and other relevant agencies, including whether an apparent violation of U.S. sanctions is voluntarily self-disclosed.”
Bitcoin cryptocurrency
As a digital currency, bitcoin enables direct, peer-to-peer payments without reliance on banks or other intermediaries. While its adoption as a medium of exchange remains limited, technologies like the Lightning Network are making payments faster and more cost-effective. These developments position bitcoin for broader use in day-to-day commerce, particularly in enabling payments that are global, final and free from geographical restrictions.
Many financial experts support their clients’ desire to buy cryptocurrency, but they don’t recommend it unless clients express interest. “The biggest concern for us is if someone wants to invest in crypto and the investment they choose doesn’t do well, and then all of a sudden they can’t send their kids to college,” says Ian Harvey, a certified financial planner (CFP) in New York City. “Then it wasn’t worth the risk.”
Nakamoto created the first Bitcoin on January 3, 2009. Bitcoin was initially mined among tech enthusiasts until the first trading markets for Bitcoin emerged in July 2010, with prices then ranging from US$0.0008 and $0.08. By then, Nakamoto transferred Bitcoin’s network alert key and control of the code repository to Gavin Andresen, who became lead developer at the Bitcoin Foundation.
Web3 is buzzing with activity. Yet, according to DappRadar, the top 15 blockchains collectively register only 165 million unique active wallets per month. The future of the space will likely hinge on finding the right balance between decentralization and innovation. It will also depend on the teams’ ability to pass on their projects to the community when the time comes.
Bitcoin rewards are halved every 210,000 blocks. For example, the block reward was 50 new bitcoins in 2009. On May 11, 2020, the third halving occurred, bringing the reward for each block down to 6.25 bitcoins. The fourth halving occurred in April 2024 and lowered the reward to 3.125 bitcoins. The next halving should happen in mid-2028 and reduce the reward to 1.5625 BTC.
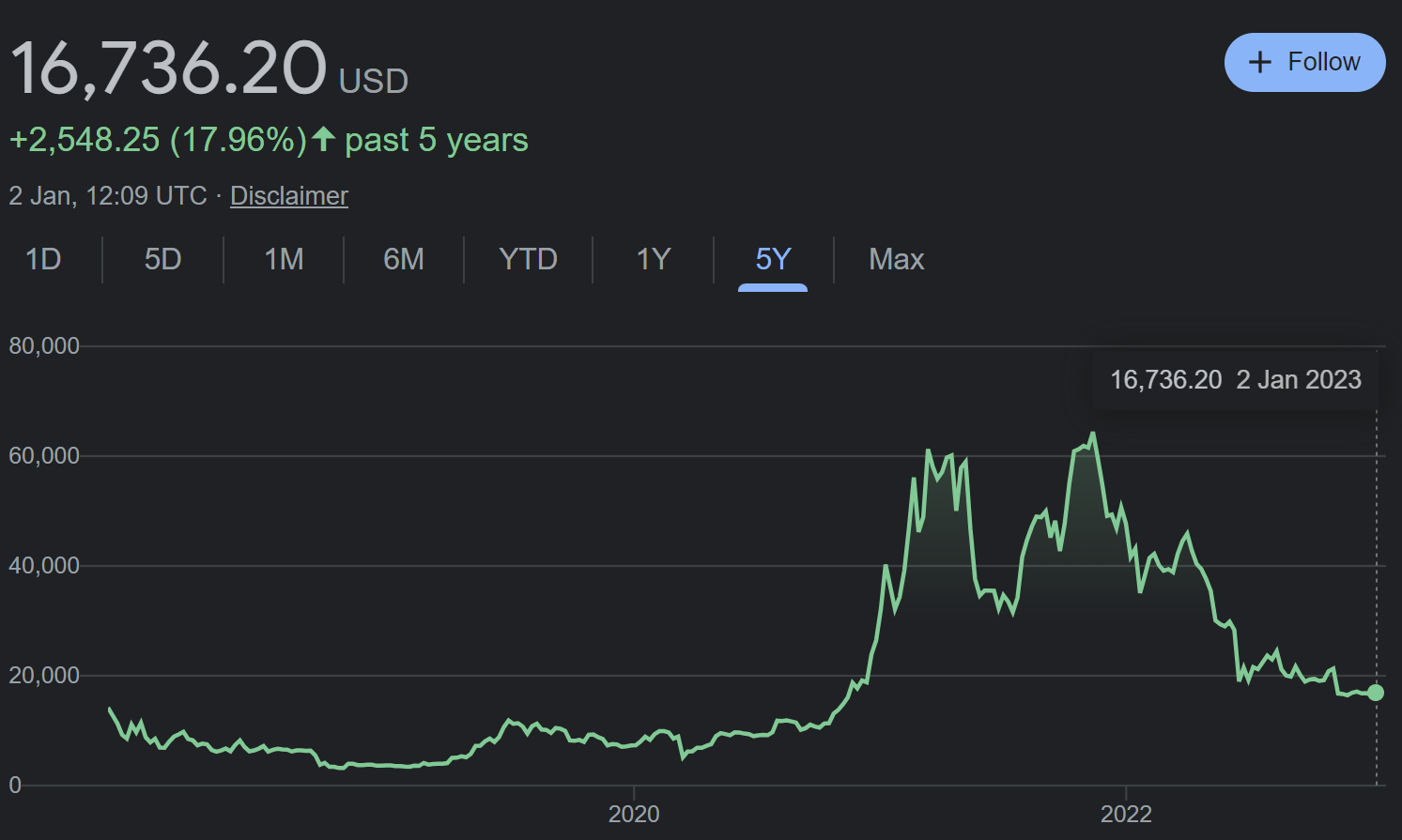
Cryptocurrency bitcoin price
On the flip side, countries like China have moved to heavily clamp down on Bitcoin mining and trading activities. In May 2021, the Chinese government declared that all crypto-related transactions are illegal. This was followed by a heavy crackdown on Bitcoin mining operations, forcing many crypto-related businesses to flee to friendlier regions.
Real estate has also embraced Bitcoin as a viable payment option. Although relatively rare, there have been notable instances of real estate sales conducted with Bitcoin. The acceptance of BTC in the real estate market showcases its growing recognition as a legitimate and valuable asset for high-value transactions. As Bitcoin continues to gain traction, more opportunities for purchasing properties using cryptocurrency may emerge.
4. Energy Consumption: Mining requires a lot of electricity to power the specialized hardware, known as ASICs. Miners often set up operations in regions with cheap electricity to reduce costs and increase profitability.
Disclaimer: This page may contain affiliate links. CoinMarketCap may be compensated if you visit any affiliate links and you take certain actions such as signing up and transacting with these affiliate platforms. Please refer to Affiliate Disclosure
You can securely store your Bitcoin in the custodial wallet on the KuCoin exchange without having to worry about managing your private keys. Other ways to store your BTC include using a self-custody wallet (on a web browser, mobile device, or desktop/laptop computer), a hardware wallet, a third-party crypto custody service, or a paper wallet.
The next Bitcoin mining event, known as the Bitcoin halving, is expected to occur around April 2028. The last halving took place in April 2024, reducing the block reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC per block. This event is significant because it reduces the rate at which new Bitcoins are created, contributing to Bitcoin’s scarcity and potentially influencing its price. The next halving in 2028 will further reduce the reward to 1.5625 BTC per block.